The pitfalls of this topic
Sea level rise: One of the most frequently mentioned consequences, which is promoted by several mechanisms.
- Because of the increased temperatures, the ice on the land is melting. Positive feedback! Permafrost soils form one of the largest carbon reservoirs on our planet. As soon as they melt, they release the CO2, which would lead to additional global warming.
- The ice in the water is also melting. Currently we still have ¼ of the sea ice we had 30 years ago.
- In addition, the water in the oceans is heated and expands as a result. Warm water is also less able to bind CO2. We would also lose the ocean as a carbon reservoir.
- Another chain reaction is caused by the fact that the additional water reduces the salinity of the oceans. This leads to changes in ocean currents, can result in floods, for example, and changes the entire ecosystem, as the ocean habitat becomes uninhabitable.
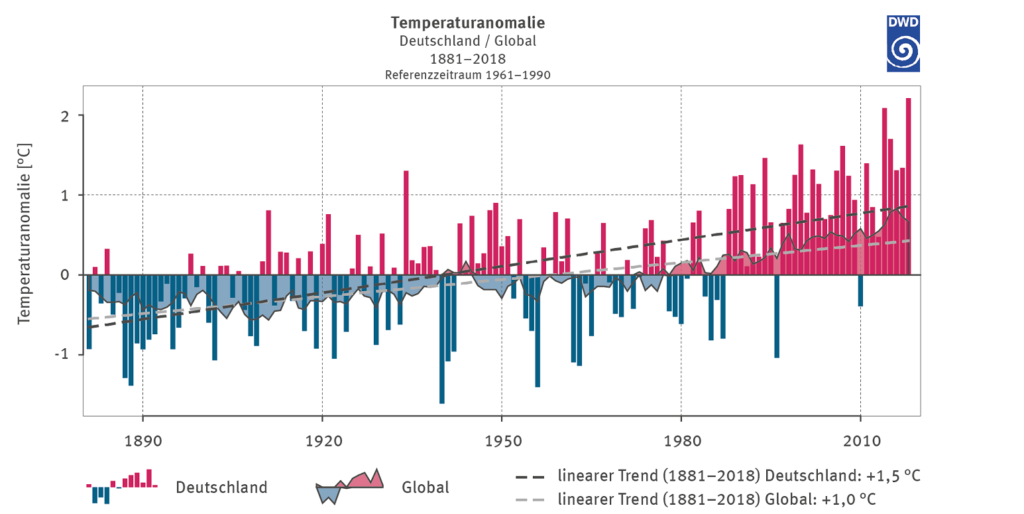
- The rise in sea level naturally also threatens the homes of millions of people. In the following diagram you can get an overview of what the situations in different countries would look like with a sea level rise of 1 metre and 5 metres.

Glaciers melt:
Another consequence of increased temperatures. Positive feedback: White surfaces reflect warming rays very effectively and thus keep the earth cool. This effect disappears, of course, when the ice melts, so that global warming (the actual cause of glacial melt) is further intensified. This effect is also called the “ice-albedo feedback effect”.
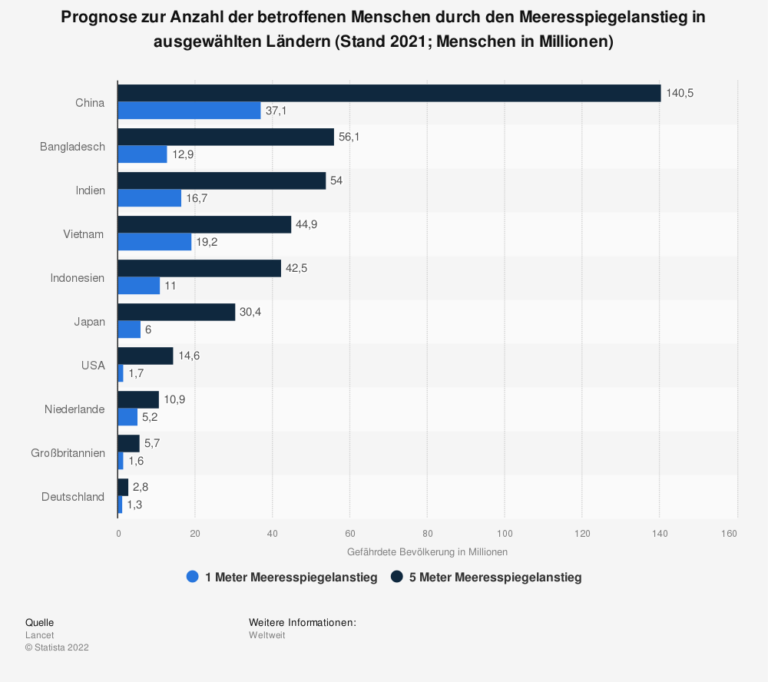
On this map you can see which areas are particularly threatened.
Indirect consequences
The direct and indirect consequences of global warming cannot always be clearly differentiated. However, some of the most important consequences caused by the above are listed below.
Ocean acidification:
- The increasing concentration of CO2 in the oceans acidifies them. This leads to the death of corals and thus also of the fish living there. With global warming of 1.5°C, this already affects 70-90% of all corals!
- This also removes the main source of food for half a billion people, as well as a widespread source of livelihood.

Drinking water shortage:Due to the rise in sea level, more salty seawater penetrates into the groundwater. Other causes: weather extremes, droughts and fires.
Starvation: Consequence of weather extremes, increased temperatures, droughts, fires
- Developing countries are particularly affected, where there is already poor or no access to water and food, and which are particularly dependent on agriculture and stable prices.
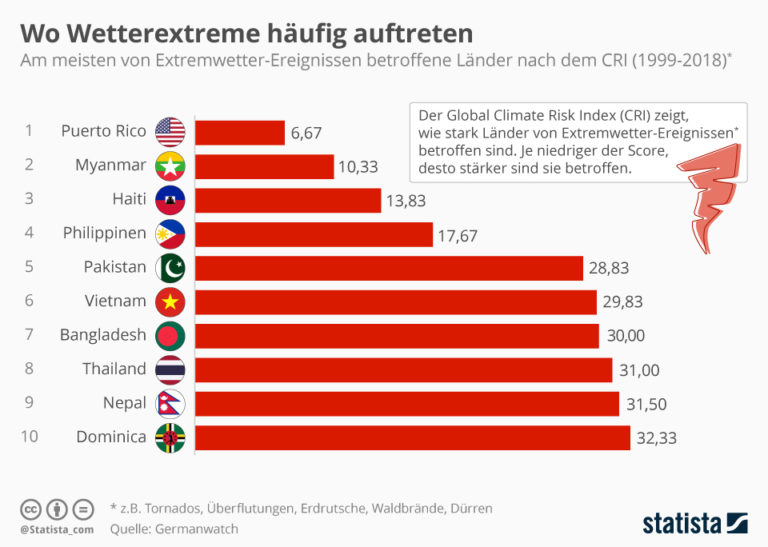
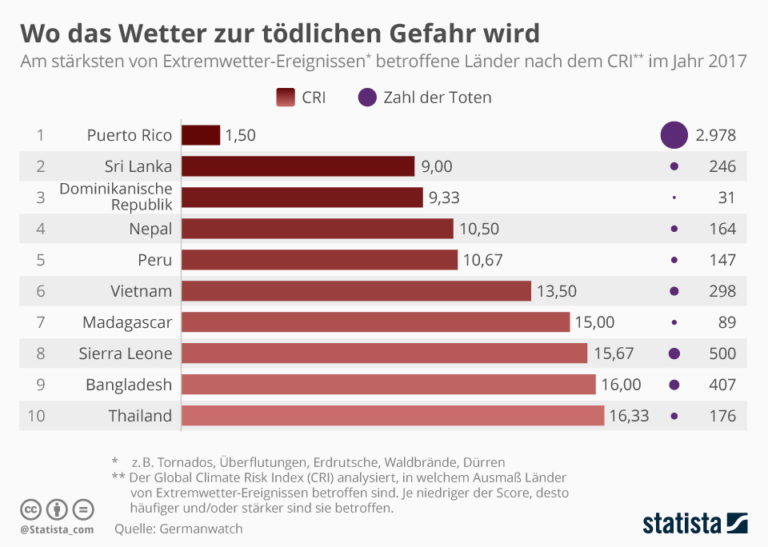
- Extreme weather events have resulted in 23.5 million people lacking sufficient food in the past year. The following graph shows you which countries are most affected.
Germany feels the impact of climate change
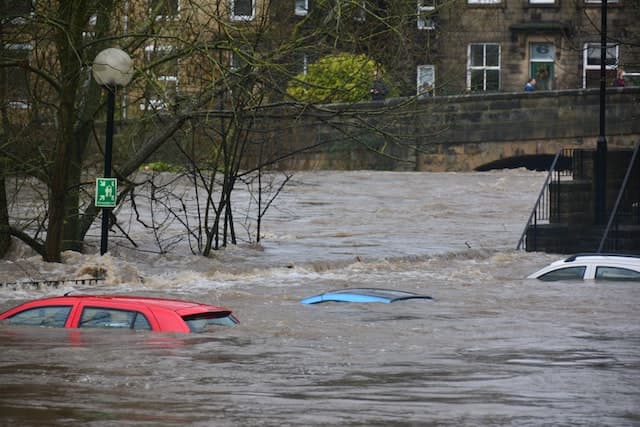
The 2021 flood disaster at the latest showed us that even Germany is not safe from the consequences of climate change. On the contrary: the more than 180 deaths and numerous people affected make us realise that we have to be active NOW. The frequency of extreme weather events has more than tripled in the last 50 years. More floods are therefore to be expected.
Lastly, we can already slowly observe changes in our seasons. The early start of spring makes our winter blues go away faster, but it also shifts the flowering season. This costs many animals food during their breeding season. In addition, there is a prolonged pollen season, which poses further health risks. The same applies to the facilitated spread of various disease vectors in the form of mosquitoes.
Positive consequences of global warming
Now it would be rather one-sided to present only the negative consequences of climate change. So, for the sake of completeness, here is an overview of the positive developments:
The expansion of new energy resources is increasing, so we are developing better alternatives to fossil fuels.
New, previously unattractive regions can profit from tourism. Good, but other regions are falling away. The Mediterranean region is no longer recommended at 40°C.
Admittedly, this pattern can be applied to most positive consequences. When Arctic ice thaws, that path is clear for shipping. Yay! Unfortunately, this area is then also free of polar bears, stored methane is released and mobile ice endangers shipping.
Well, that was sobering: the negative consequences undoubtedly outweigh the positive ones. So let’s move on to ways to stop climate change.
How can we respond?
Our options for action are limited to three types of behaviour:
- Mitigation: This refers to combating the causes, in this case the prevention of negative impacts on the climate. In order to stop the consequences of climate change, we would have to reduce our CO2 emissions, consume less, or reforest forests, for example. Most measures for “climate protection” belong to this category.
- Adaptation: Addressing the impacts of climate change involves adapting to its risks, in other words, learning to live with the problem. Good examples of this are the construction of dams and other types of flood protection, or adaptation in building construction.
- Geoengineering (Climate Engineering): “Fixing” the problem by, for example, taking CO2 out of the atmosphere or counteracting ocean acidification. This way solves the problem that the climate might respond too slowly to our climate protection measures. Accordingly, geoengineering could be an alternative to avoid tipping points. However, its development is still in its infancy, so that costs and effectiveness are sometimes difficult to predict.
What can you do?
We often hear that we have to act now. We hear less often that we really have to act NOW, because immediate climate protection measures take decades to show their effect.
So: It is better to act green than to see black! In the following, we suggest how to do this.
Food
When it comes to food, there are many ways you can easily reduce your CO2 emissions. Next time you go shopping, try implementing 3 of the tips and see what new dishes reveal themselves to you! So:
- Really enjoy your meat by going for better quality, but less often.
- Otherwise, go for fresh fruit and vegetables, pulses and nuts. Not only the environment, but also your body will thank you!
- Regional and seasonal food is much kinder to our environment and gives you more nutrients. Seasonal calendars, like the one from Utopia, show you what is growing.
- There is huge waste in the food industry because crooked, naturally grown fruit and vegetables are no longer available in our shops. Etepetete and SIRPLUS save these foods and put a smile on your face with the crookedest carrots!
- Currently, more than half of German food waste is avoidable. At TooGoodToGo and RESQ you can find whole dishes from restaurants that you can save from the bin at a lower price.
- Next time you go to a restaurant, bring a can if you know the portions are usually too big for you. Or ask to have your leftovers packed on the spot!
- To use your leftovers at home, EatSmarter, Zu Gut für die Tonne and the recipe app from Essen und Trinken suggest creative recipe ideas.
- If you regularly buy too much: Write shopping lists, freeze or give the surplus to neighbours and friends.
- After the best-before date, your food is not directly waste. Smell it to find out if you can still use it!
Energie use
Reduce your energy consumption and, if possible, switch to green electricity! There is a lot of waste, especially at home, but it can be improved quickly by making small habitual changes. Simple tricks include:
- Boil only as much water as necessary.
- Replace normal light bulbs with LED bulbs (you can save 90 % of your energy consumption for lighting! And up to 200 € electricity costs…).
- Save 30% of your fridge’s electricity consumption by defrosting it. Also, let dishes cool down completely before you put them away.
- Adjust the energy settings of your electronic devices, keyword power saving mode and do without standby mode. And take the power supply out of the socket!
- Save yourself the prewash. What’s more, 30°C washes use only a third of the electricity of 60°C washes and get just as clean. Only underwear, towels and bed linen should be washed hotter.
With the help of the Klima Buddy app, you can see where YOU can best save CO2 in your private life!
Environmentally conscious travel
You’re already aware of the CO2 emissions from airplanes and cars, but here’s the suggestion again: it’s better to opt for buses, trains, and bicycles. It’s highly effective because you can likely make this choice daily!
Finances
Conclusion
To answer the initial question, the consequences of climate change are severe and affect all areas of life. Climate extremes, rising average temperatures, rising sea levels, droughts, floods and melting glaciers can be summarised as direct consequences. However, they bring with them other impacts, some of which exacerbate each other. Although the most severe consequences have so far occurred in developing countries, Germany is also increasingly affected. We can still change this. Each of us has the power to make a big difference with small adjustments. In the truest sense of the word, the life of humanity is now in our hands.
We are looking forward to hearing from you: Which consequences of climate change have you already experienced? Which ones are you particularly worried about? And would you like to share more tricks? Then feel free to write to us via the contact form.




